# Introduction
Football positions, defense and offense alike, are the backbone of every strategy on the field. Whether you’re a budding athlete, passionate fan, or simply curious, understanding these roles unlocks deeper appreciation for the beautiful game. In this article, I’ll break down key positions, strategic importance, comparisons, common mistakes, and a practical guide to recognizing roles during any match.
# What Are Football Positions Defense and Offense?
Football positions fall into two main categories: defense and offense. Defense seeks to stop goals, offense aims to score them. Each category features specialized roles, like center-back or striker, all working in sync.
Teams typically use eleven players, arranged in tactical formations (e.g., 4-4-2, 3-5-2) to maximize strengths. According to FIFA statistics, the most used formation globally in 2023 was the 4-3-3, emphasizing balance between defensive solidity and offensive flexibility (SOURCE: FIFA Global Report 2023).
# Main Defensive Football Positions Explained
Let’s break down the main defensive positions:
Goalkeeper: This is the only player allowed to use hands within the penalty box. Their job is simple — stop the ball from entering the net.
Center-Backs: Standing in front of the keeper, they intercept attacks and clear threats. Most elite teams use two center-backs.
Full-Backs: Located on both flanks, full-backs defend against opposing wingers and often join attacks.
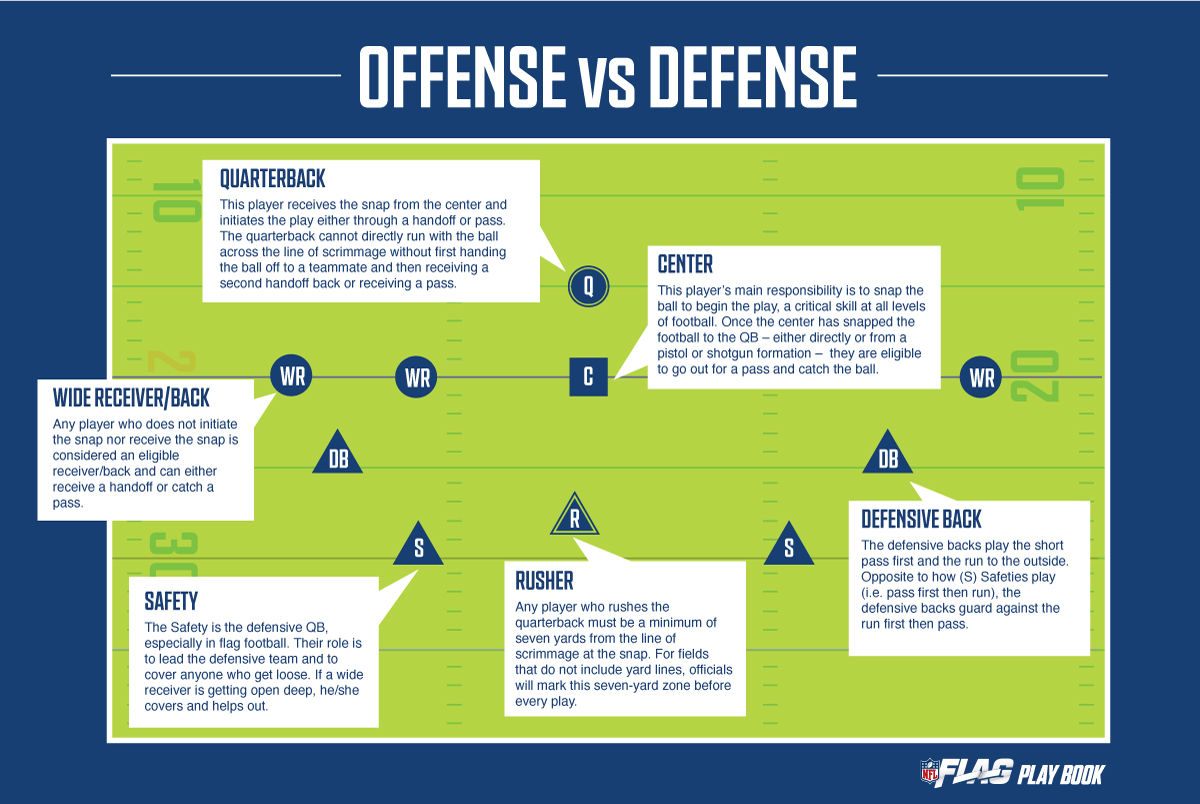
Defensive Midfielder: Positioned ahead of defenders, interrupts opponent plays and distributes the ball forward.
According to UEFA, 68% of top European teams use a dedicated defensive midfielder to increase their ball recovery rate (SOURCE: UEFA Tactical Trends 2023).
# Main Offensive Football Positions Unveiled
Attacking roles bring creativity, speed, and finishing prowess:
Strikers (Center Forwards): These are the goal machines standing closest to the opposition’s net.
Wingers: Out wide, wingers stretch defenses and deliver crosses.
Attacking Midfielders: Connecting midfield and forwards, they create chances through passing, dribbling, and vision.
Second Forward: Supports the striker, exploits gaps, and presses defenders.
Depending on tactics, teams may use different combinations, like a “false nine” or two strikers.
# Key Differences: Defense vs Offense (HTML Table)
To clarify differences at a glance, see the table below:
| Feature | Defense | Offense |
|---|---|---|
| Main Objective | Prevent goals | Score goals |
| Typical Positions | Goalkeeper, Center-back, Full-back, Defensive midfielder | Striker, Winger, Attacking midfielder, Second forward |
| Skill Focus | Tackling, positioning, leadership, composure | Shooting, dribbling, speed, creativity |
| Main Area Covered | Own half, penalty box | Opponent half, attacking third |
# Step-by-Step Guide: How to Identify Football Positions During a Game
Want to recognize each position in action? Here’s a quick guide:
1. Observe formation lines before kickoff. Defenders stay closest to their goal.
2. Spot the goalkeeper — usually wearing a contrasting jersey and gloves.
3. Watch for players intercepting and clearing balls; they’re defenders.
4. Notice who advances quickly into enemy territory; those are offensive positions, like wingers and strikers.
5. Track passing combinations. Midfielders, including defensive and attacking types, often control tempo and link defense to offense.
When our team analyzes game footage, we focus on movement patterns, positioning, and action zones to accurately assign each player’s primary role.
# Common Pitfalls in Understanding Football Positions
WARNING: Misclassifying football positions defense and offense can lead to tactical errors! Here are frequent mistakes:
ASSUMING ALL DEFENDERS NEVER ATTACK: Modern full-backs and even center-backs join attacks during set pieces.
IGNORING MIDFIELD’S DUAL ROLE: Midfielders can be both defensive anchors and offensive creators.
CONFUSING WINGER WITH FULL-BACK: Wingers attack wide areas, full-backs defend them.
OVERLOOKING FORMATION FLUIDITY: Players may switch roles as tactics evolve during a game.
# Real-World Case Example
Let’s take Liverpool FC. Their right-back, Trent Alexander-Arnold, frequently pushes forward, acting almost as a playmaker despite his nominal defensive role. This tactical evolution blurs traditional lines between football positions defense and offense. Such role versatility is why modern teams succeed.
# Expert Insights: Why Mastering Football Positions Matters
According to my experience training youth teams, knowing each position’s nuances not only improves player development but enhances tactical adaptability. When you watch pros, notice how specialized movements and quick transitions define each role. This expertise translates into smarter viewing and coaching.
# Football Positions Defense and Offense: Practical Checklist
Use this quick checklist to master football positions:
FAMILIARIZE WITH STANDARD FORMATIONS (E.G., 4-4-2, 4-3-3)
IDENTIFY DEFENSIVE AND OFFENSIVE POSITIONS BEFORE EACH MATCH
PAY ATTENTION TO PLAYER MOVEMENTS AND AREAS COVERED
NOTICE TACTICAL CHANGES; FLEXIBLE ROLES ARE COMMON
REVIEW MATCH FOOTAGE TO SPOT POSITIONAL ERRORS AND TRANSITIONS
# Conclusion
Mastering football positions defense and offense unlocks deeper tactical understanding and elevates your game appreciation. Whether watching or coaching, remember that positions aren’t static — strategy, movement, and adaptability shape every second on the pitch. Dive in, observe, and keep learning the beautiful details behind every team’s lineup.